Our researchers are committed to creating a sustainable future that is centred on the circular economy philosophy and the need to reduce carbon emissions.
Circular economy philosophy diagram
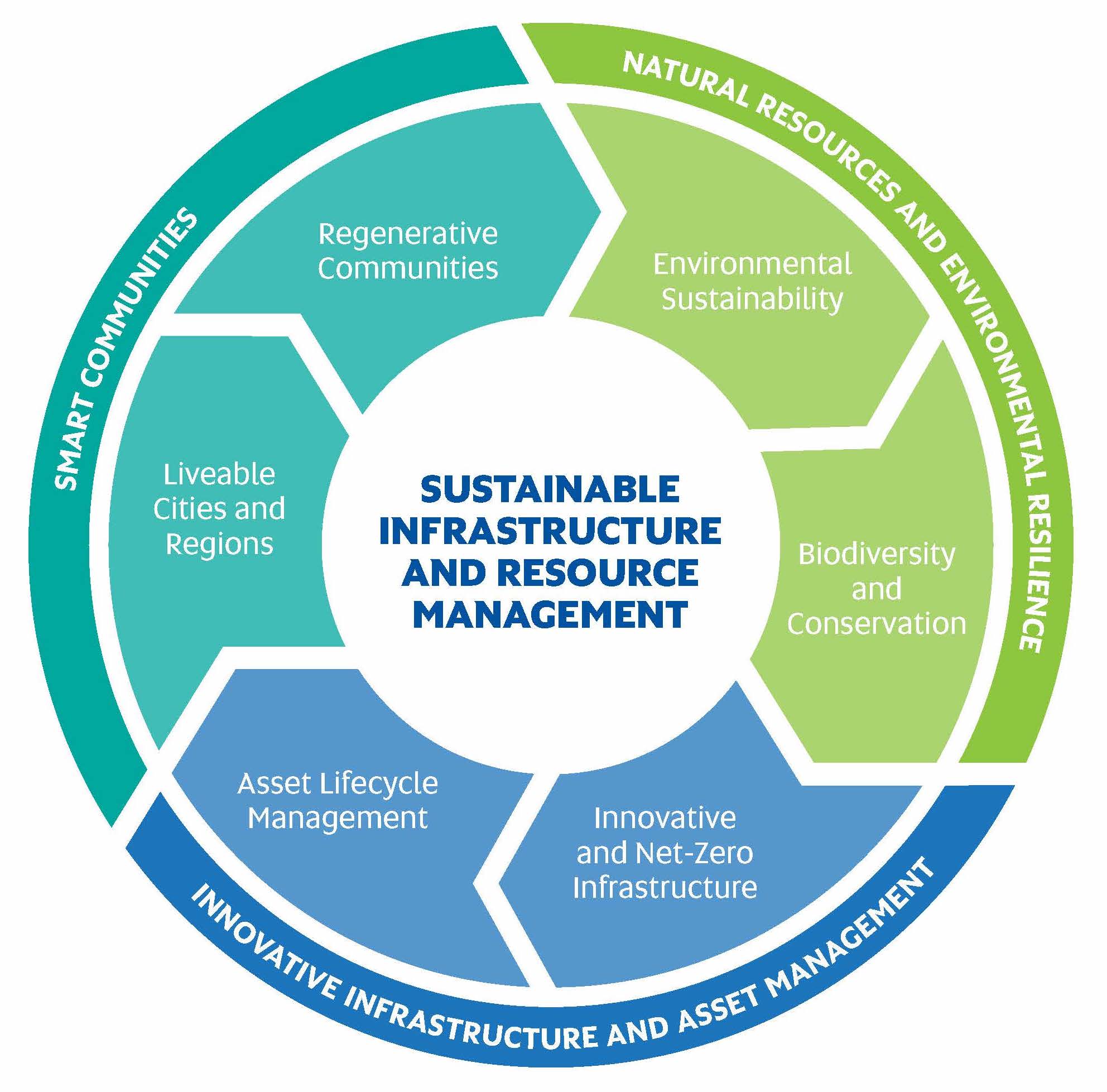
Research Streams
Our research is focused on physical infrastructure management and the sustainable management of assets. Our research is organised into three streams, with six main topics of research:
Research outputs and facilities
Our members regularly publish their research, sharing their knowledge and findings in journals, conferences and workshops. These publications contribute to new knowledge, have changed practices, and forged meaningful connections both within and outside of academia. SIRM also like to involve industry to utilise their research facilities.
Details of the publications produced by members of SIRM can be found in the links below. Additional information about specific authors or outputs is available from the University of South Australia Research Outputs Repository.
-
Precinct Carbon Assessment Tool
The Precinct Carbon Assessment (PCA) tool, developed by a research team at UniSA, aims to provide design and planning decision support to initiatives for (re)development of low carbon precincts. Subsequent enhancements have expanded its scope, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of precinct lifecycle energy and cost performance. This tool facilitates the examination of various aspects including embodied, operational, and travel-related energy consumption, carbon emissions, and costs. Furthermore, it incorporates an analysis of the carbon offset and cost savings provided by rooftop renewable energy generation units like solar PV and solar hot water systems.
A key advantage of this tool is its incorporation of precinct morphology, which integrates inter-building effects (IBE) into analyses involving daylighting, HVAC, solar access, and traffic impacts. These considerations directly inform optimal planning decisions for precincts. Additionally, the tool offers a detailed assessment at the building elements level and allows for customisation of appliance scheduling, thereby promoting applications of green building products and materials as well as efficient use of high-energy appliances.
Originally developed on the Matlab GUI platform, the full version of the PCA tool is downloadable for local installation. For demonstration purposes, a web-based light version, featuring selected functional models, is accessible online."
-
Machine learning application using high performance graphical processing unit (GPU) workstation
Our researchers utilise image processing, data analytics, and machine learning to support R&D activities in sustainable infrastructure and resource management. In addition, we possess technical expertise in utilising large-scale scientific instruments and computational facilities, such as the Australian Synchrotron, Australian Nano Fabrication Facility, and High Performance Computing resources. SIRM's technical proficiency extends to optical physics, robotics vision, automation, embedded systems, and GPU-accelerated machine learning, to support projects focused on natural resources, environmental resilience, innovative infrastructure, and asset management.
-
World Sufficiency Lab and relationship to Adaptive Reuse
The pursuit of sufficiency, avoiding demand for natural resources while ensuring well-being for all with planetary boundaries, is crucial in limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees and meeting other UN Sustainable Development Goals. After establishing a research direction, SIRM played a key role in co-hosting the 1st International Sufficiency Summit in May 2023, with the aim of learning from French policies and experience and promoting the concept globally. Co-organised by Prof David Ness, with the assistance of Assoc Prof Ke Xing, the summit featured urban and human settlements as the main strand, with the Lord Mayor of Adelaide participating in a panel discussion.
With his French colleague and IPCC lead author Dr Yamina Saheb, Prof Ness subsequently co-founded the ‘World Sufficiency Lab’ (WSL), Paris, with urban settlements - including the built environment and infrastructure – again comprising a principal theme. In addition to the WSL Paris, regional ‘Sufficiency Communities’ are being established, with Adelaide forming the hub of a community to serve Australasia and beyond. The activities will closely align with SIRM research on resource management in buildings and infrastructure, with sufficiency forming an important addition to previous research with Arup on circularity in the built environment.
In particular, the City of Adelaide and State Government are jointly pursuing adaptive reuse of existing vacant and underutilised city buildings for housing, under the leadership of the Lord Mayor of Adelaide. Recent Adelaide-Paris discussions have centred on using Adelaide as a pilot study for the WSL, enabling Adelaide to benefit from international know-how and vice-versa. This is expected to open up research opportunities for SIRM, utilising the Precinct Carbon Assessment (PCA) tool and connected with current research on saving energy and reducing embodied carbon.
-
Water Treatment Control – Coagulant Dose Prediction APP
The coagulation optimisation model WTC-Coag has proved to be a useful tool for coagulation optimisation at conventional drinking water treatment plants. It has been used to help guide water treatment plant managers to select the primary coagulant dose at Adelaide metropolitan drinking water treatment plants for several years. The APP requires raw water turbidity, colour, and UV absorbance at 254 nm as input data, values are then used to produce coagulation predictions. The generic nature of the software (no site-specific calibration required) can be highly beneficial for the optimisation of coagulation at other water treatment plants.
Software Link
WTC-Coag Water Treatment Control for Coagulation (streamwtc.com)




