Carbon-free renewable energy solution to ‘heat up’ industry
By Dan Lander
 TECHNOLOGY AND ENGINEERING A system developed at UniSA uses renewable energy from solar or wind to generate heat, which is stored in a bed of rocks and phase change materials, so it can be available on demand for high temperature applications such as paper milling, agriculture, mineral operations and food production
TECHNOLOGY AND ENGINEERING A system developed at UniSA uses renewable energy from solar or wind to generate heat, which is stored in a bed of rocks and phase change materials, so it can be available on demand for high temperature applications such as paper milling, agriculture, mineral operations and food productionUniSA researchers have developed a new technique that may greatly reduce industry’s dependence on natural gas, combining renewable energy and low-cost thermal storage to deliver heat for high-temperature industrial processes.
Research indicates about 20 per cent of global fossil fuel emissions are produced by industry, largely through burning natural gas to create heat for various processes in the manufacture of products such as paper, chemicals and mineral goods.
Industry is the third largest contributor (after transportation and electricity) to greenhouse gas emissions in the world, and as such, faces mounting pressure to reduce its carbon footprint.
Researcher Rhys Jacob from UniSA’s Barbara Hardy Institute says the system developed by his team can deliver industrial heat at temperatures between 150 and 700°C using renewable energy from solar or wind combined with a novel approach to energy storage.
“Rather than trying to store renewable electricity in a battery, our system uses electricity to generate heat and then stores that heat in a bed of rocks and phase change materials, so it can be available on demand for high temperature applications,” Jacob says.
“We can currently deliver temperatures up to around 700°C, which is adequate for many processes in industries like paper milling, agriculture, mineral operations and food production.”
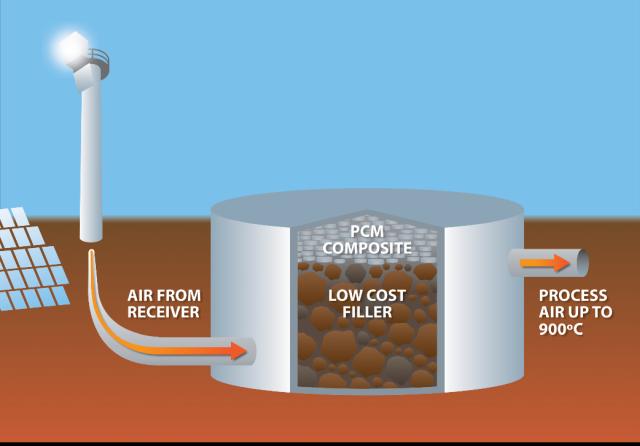 The system stores heat in a bed of rocks and phase change materials for later use
The system stores heat in a bed of rocks and phase change materials for later useIn addition to the environmental benefits of emissions-free operation, the system is also economically competitive, offering potential savings against increasingly unstable gas prices and more cost-effective storage than battery technology.
“Gas prices have gone through the roof lately, which is a key incentive for industry to find alternatives, and storing heat is also a magnitude or two cheaper than storing energy in batteries,” Jacob says.
Despite its industry-changing potential, the technology is comprised of relatively basic components, meaning initial installation costs are low, and ongoing maintenance requires no specialist expertise or costly replacement parts.
“One key advantage of this system is current staff in most operations could maintain it without any training, which ensures it is extremely easy to integrate into an existing business,” Jacob says.
This easy integration also ensures the system can operate in conjunction with existing gas-fired heating units, providing manufacturers greater flexibility and reliability in the production cycle.
“The heat storage capacity in the system should be sufficient to cover most fluctuations in renewable energy input, but if at times there is a shortfall, gas could still be brought online as needed.
“Similarly, you could use our system as a pre-heater in applications like cement production, which requires air temperatures up to 1400°C.
“In both these scenarios, the combination of our system with existing technology could see a significant reduction in operating costs and greenhouse emissions,” Jacob says.
The research team currently has a working prototype located at the Barbara Hardy Institute at Mawson Lakes, and is developing a second, slightly refined version of the system that should be suitable for full commercial operation.
Other research around the project is leading to potentially ground-breaking advances in the thermal storage capacity of phase change materials and the efficiency of heat-to-energy conversions, indicating growing opportunities for innovation in related areas.
Other Stories
- Painless needles on the way for vaccinations
- Hi. How can I help you? Health clinic embraces the robot age
- Virtual health coach ‘Paola’ will help you get fit and eat well
- Carbon-free renewable energy solution to ‘heat up’ industry
- From the Vice Chancellor
- Achievements and Announcements
- The technology to take a jury into a 3D crime scene
- Oscars 2019 plays it safe with Green Book, lacks enlightened thinking
- Organ-on-a-chip technology to reduce side effects of radiotherapy
- Find out about UniSA’s dedicated student support services (Video)
- International defence research lab with France planned for Adelaide
- New innovation hub in Whyalla to nurture regional startups
- The latest books from UniSA researchers
- In Pictures




